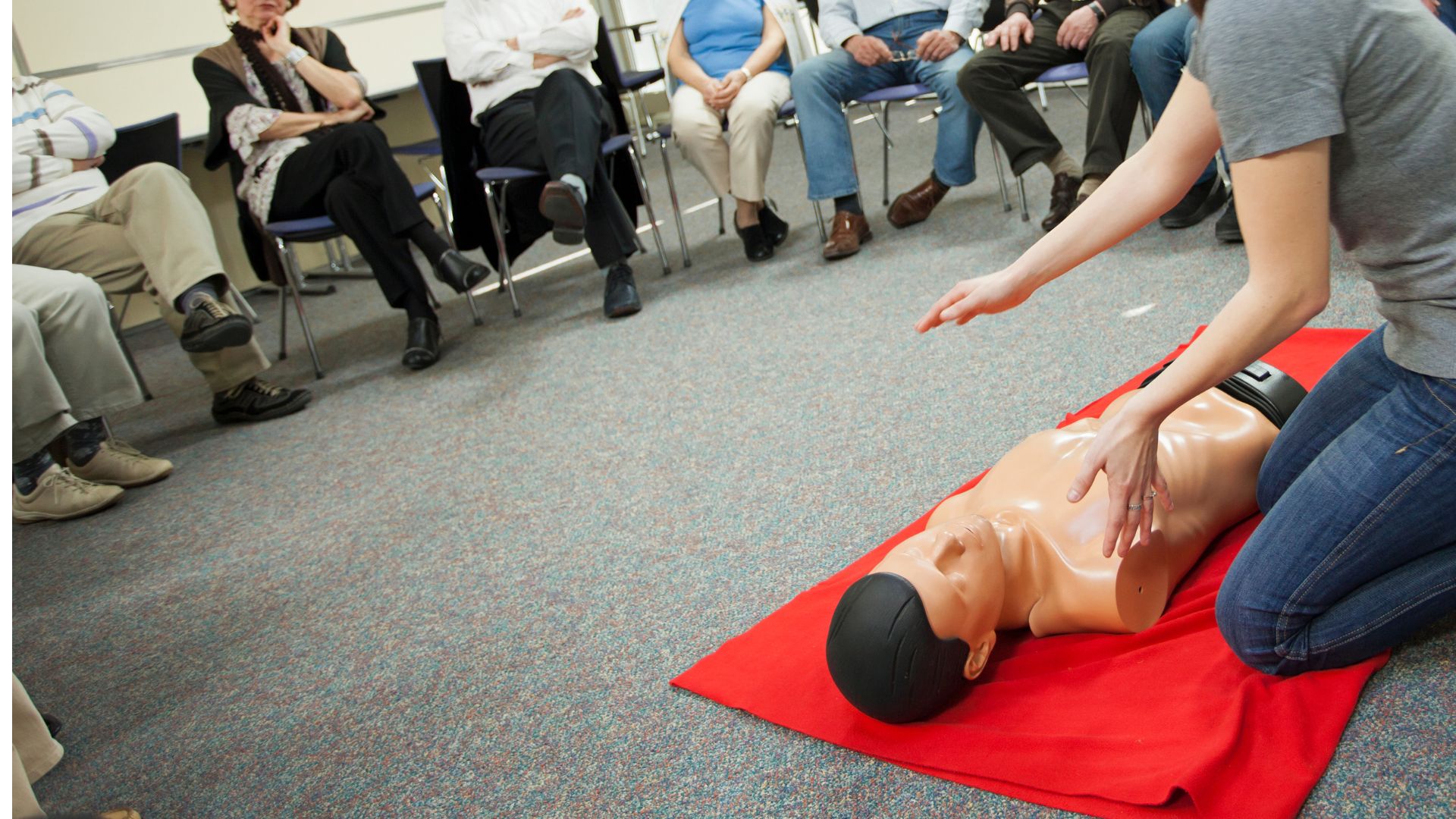
CPR is truly an amazing method that we should practice more. Ever since the 1960s, CPR is an integral part of emergency medical care. With its potential to save lives, everyone and everywhere should be familiar with CPR and have the knowledge to perform it.
So, are we really at a point where we think of CPR as a basic life skill? Unfortunately, no. Around 37% of millennials would rather spend time on Instagram than learn anything related to heart health.
As unique of a state as Texas is, the need for CPR remains a challenge. For example, only 29% of the predominantly Hispanic population in El Paso who suffered a cardiac arrest received bystander CPR. Each of us can make a difference by learning the CPR guidelines for Texas, and this article is your guide to equipping you with all the necessary knowledge.
Understanding CPR and its Importance
After careful evaluation, we assume that the problem lies in not enough people understanding the role of CPR. You’ve heard about it, and you’ve probably even watched reviving movie scenes on TV. But you’ve never really understood its real-life importance.
First of all, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) helps restore blood flow. In cases of cardiac arrest, the heart will stop pumping blood effectively. With or without CPR, most cardiac arrest survivors have some level of brain injury and impaired consciousness. However, CPR can potentially help stop an irreversible brain injury.
Professional medical care will not be available at all times. CPR is the only thing that can help an OHCA patient survive in such cases. Otherwise, the outcome will be fatal. So, this means CPR is crucial for buying time until an ambulance arrives.
Each year in the US, over 365,000 cardiac arrests occur outside of hospital settings. And oftentimes, bystander CPR isn’t provided because people have never completed CPR certification courses or even glanced at the CPR guidelines.
All in all, by performing CPR, you can save someone’s life. You can be the thin line between life and death. And that’s more than enough to make CPR one of the basic life skills everyone should learn.
Following the Official CPR Guidelines in Texas
In Texas, you’ll be trained to follow the official CPR guidelines either set by the American Heart Association or the American Red Cross. Expect to learn the following aspects:
-
- Chest Compressions. One thing a CPR technique can’t go without is chest compressions. Once you ensure the scene is safe and you place the patient on a flat surface, you can proceed with administering chest compressions. You should do this at a steady rate by providing 100-120 compressions per minute.
-
- Rescue Breaths. After a cycle of 30 chest compressions, administer 2 rescue breaths. However, if you don’t feel confident or have never taken a CPR course, it’s better to stick to hands-only CPR.
-
- Automated External Defibrillator (AED). You’ll, of course, be instructed on how to use an AED. According to the AHA, approximately 50% of individuals aren’t able to locate an AED at work. Therefore, it’s important to receive proper training on AED usage to increase the chances of OHCA patients surviving.
-
- Recognizing Cardiac Arrest. Often, individuals find it hard to make a difference between a cardiac arrest and a heart attack. And performing CPR on a person who’s suffering a heart attack can be fatal. That’s why it’s important to recognize the signs when a cardiac arrest is about to happen.
To increase the number of patients receiving bystander, as well as EMS CPR, the public health strategies of Texas suggest implementing CPR/AED programs in schools and promoting community-based group training. They also want to encourage businesses, restaurants, and other community settings to have AEDs available.
In El Paso, all personnel responsible for taking care of patients are required to receive CPR training following the guidelines of the American Heart Association. Thanks to the TTUHSC El Paso, they can all take free CPR classes on a monthly basis, with priority for those who need Basic Life Support (BLS) Certification.
CPR Guidelines by the American Heart Association
Even though the main aspects and the goal – saving lives – are practically the same, both AHA and ARC have their own guidelines. The AHA is renewing its guidelines every five years. Here are the newest ones released in 2020:
-
- Check if the scene is safe enough to perform the CPR technique.
-
- Check if the patient is responsive. If not, immediately call 9-1-1 or have someone else nearby do it.
-
- Check for AED availability and other emergency equipment.
-
- Check for irregular breathing and pulse. If you can feel the pulse and the patient’s breathing pattern is normal, monitor the situation until professional medical help arrives.
-
- If you can feel the pulse, but the breathing is irregular, start administering rescue breaths at the rate of 1 breath every 6 seconds. Simultaneously check their pulse. If you can’t feel it, start with CPR.
-
- If the patient is gasping and you can’t feel their pulse, start with the full CPR technique. Start with 33 chest compressions, then give 2 rescue breaths. If there’s an AED, use it as soon as possible. Don’t stop until help arrives or the patient becomes responsive.
CPR Guidelines by the American Red Cross
The American Red Cross provides both online and in-class CPR training in Texas. Upon completion, you’ll receive full certification.
The organization offers CPR training designed specifically for the needs of schools in Texas, allowing all staff, including teachers and board members, to not only learn the basics of CPR but also be able to pass on the knowledge to their students.
Same as the AHA, the Red Cross is also renewing its guidelines every five years. Let’s take a look at the CPR steps, as per the American Red Cross guidelines published in 2022;
-
- Check if the scene is safe to perform CPR and use personal protective equipment if possible.
-
- Check if the patient shows any signs of responsiveness. Are they breathing? Are there any life-threatening wounds on their body?
-
- If the person is only gasping and isn’t showing any signs of responsiveness, call 9-1-1 or get someone else to do it.
-
- Lay the patient on a flat and firm surface and kneel beside them.
-
- Start performing 30 chest compressions at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute with your elbows locked and your hands centered on the patient’s chest.
-
- Provide 2 rescue breaths after every 30 chest compressions.
-
- Continue the procedure until professional help arrives or the cardiac arrest patient becomes responsive.
CPR Requirements for Schools in Texas
The importance of CPR in schools cannot be overlooked. If there’s a place one should expect to feel safe, it’s within an educational institution. Naturally, it’s recommended for all schools in Texas to raise awareness about CPR as a life-saving technique. According to the Texas Legislature, the latest CPR requirements for schools in Texas are as follows:
-
- Schools must provide CPR and AED instructions to students in grades 7 through 12, as set by the State Board of Education (SBOE) and section 28.0023 of the Education Code.
-
- CPR training should only cover CPR and AED techniques following the guidelines set by widely recognized organizations, such as the American Heart Association and the American Red Cross.
-
- It’s not mandatory to have a CPR/AED certification. However, if there’s a need for one, the training instructor must be certified by the American Red Cross or the American Heart Association.
-
- The Texas Education Agency (TEA) is allowed to accept donations to support CPR/AED instructions. The same goes for school districts.
These requirements will come into force starting from the 2023-2024 school year. It’s important for every school to implement them if they want to create a safer environment for their students. For teachers required to hold a certification in Adult, Child, and Infant Pediatric CPR/AED, and First Aid, they’re allowed to take the course on-site, online, or through a combination of both.
Bottom Line
As in every other state in the US, the CPR guidelines in Texas play a huge role in helping you master the CPR technique. The Texas Legislature has set clear requirements for CPR instruction in schools, ensuring that students receive the best possible training.
Also, Texas is following CPR guidelines set by the American Heart Association and the American Red Cross. And by following these guidelines, you can raise awareness of the importance of CPR in your community and potentially save someone’s life.